-
Table of contents
- 1. Task Inspector
- 2. Compare Projects
- 3. Timeline View
- 4. Grouping Tasks
- 5. Custom Fields
- 6. Critical Path Highlighting
- 7. Network Diagram View
- 8. Earned Value Analysis
- 9. Resource Leveling
- 10. Auto Filtering
1. Task Inspector
This feature helps identify issues that may impact the schedule, such as overallocated resources or scheduling conflicts, and provides suggestions for resolving them.
To view the Task Inspector in Microsoft Project, follow these steps:
- Open your project in Microsoft Project.
- Select the task that you want to inspect or analyze.
- Go to the "Task" tab in the ribbon at the top of the window.
- In the "Task" tab, you will find the "Inspect" group.
- Click on the "Task Inspector" button in the "Inspect" group

You can expand or collapse the sections within the Task Inspector pane to view the relevant information. The Task Inspector is a valuable tool for project managers to analyze and troubleshoot tasks, ensuring smooth project execution and scheduling.
2. Compare Projects
This allows you to compare two different versions of a project plan to identify the differences between them and track changes made over time.
How to compare projects
To compare projects in Microsoft Project and identify the differences between them, follow these steps:- Open Microsoft Project and open the two projects you want to compare.
- Go to the "Report" tab in the ribbon at the top of the window.
- In the "Report" tab, click on the "Compare Projects" button in the "Project" group.
- The "Compare Project Versions" dialog box will appear. In this dialog box, you will be able to select the version, that you want to compare your current schedule with.
- Then you can select the fields that you want to compare in the Task and Resource Tables.
- Finally click on the "OK" button in the "Compare Projects" dialog box.

Comparing projects in Microsoft Project allows you to track changes made over time and understand the variances between project versions. It helps you stay informed about project updates and make informed decisions based on the comparison results.
3. Timeline View
This feature lets you create a high-level, visual representation of your project schedule, which can be easily shared with stakeholders through copy-pasting into other Office applications like PowerPoint or Word.
How to use the timeline feature
To use the Timeline feature in Microsoft Project and create a visual representation of your project schedule, follow these steps:- Open your project in Microsoft Project.
- Go to the "View" tab in the ribbon at the top of the window.
- In the "View" tab, click on the "Timeline" button in the "Split View" group. This will open a blank Timeline view at the top of the Microsoft Project window.
- By default, the Timeline will show the duration of your entire project. You can adjust the timeline's start and end dates to focus on a specific period by dragging the handles at the ends of the timeline.
- To add tasks to the Timeline, select the tasks you want to include by clicking on them in the Gantt Chart or Task Sheet view. You can select multiple tasks by holding down the Ctrl key while clicking on the tasks.
- With the tasks selected, right-click on one of them and choose "Add to Timeline" from the context menu. The selected tasks will be added to the Timeline.
- Once the tasks are added to the Timeline, you can further customize the appearance and level of detail by right-clicking on the Timeline and choosing "Format Timeline" from the context menu. This allows you to adjust the font size, date format, task bars, and other visual settings.
If you want to share the Timeline with others, you can copy and paste it into other Office applications like PowerPoint or Word. Simply select the entire Timeline or a portion of it, right-click, and choose "Copy Timeline" from the context menu. Then, navigate to the desired application and paste the Timeline.
The Timeline feature in Microsoft Project allows you to create a high-level, visual representation of your project schedule. It helps stakeholders and team members quickly understand the project's timeline, key tasks, and milestones. By customizing the Timeline view, you can present the project schedule in a clear and concise manner, facilitating effective communication and collaboration.
4. Grouping Tasks
Organize tasks by specific attributes, such as resource, priority, or deadline, to get a better understanding of the project's structure and progress. To group tasks in Microsoft Project follow these steps:- Open your project in Microsoft Project.
- Go to the "View" tab in the ribbon at the top of the window.
- In the "View" tab, go to the Data group and select the dropdown that shows "[No Group]".
- Select one of the built-in groups or create a new group.
- To clear your group use "Clear Group" in the dropdown.
5. Custom Fields
Create custom fields to capture unique project information, such as cost codes, risk levels, or any other data relevant to your specific project management needs.
How to create custom fields
To create custom fields in Microsoft Project follow these steps:- Open your project in Microsoft Project.
- Go to the "Project" tab in the ribbon at the top of the window.
- In the "Project" tab, click on the "Custom Fields" button in the "Properties" group. This will open the "Custom Fields" dialog box.
- In the "Custom Fields" dialog box, choose whether you want to create a task or resource field and then select the type of field from the "Type" dropdown menu. The available types include Text, Number, Cost, Date, Duration, Flag, and more.
- Next click on the row number where you want to add a custom field. Each row represents a different custom field.
- Click rename to choose a descriptive name that reflects the purpose of the field.
- Under "Custom attributes", you can optionally specify a lookup table or formula to populate the values in the custom field. This is useful for creating dropdown lists or calculating values based on other project data.
- Set the desired properties for your custom field under the remaining headings, we suggest choosing "None" unless you have a specific use case that needs these options.
- Click "OK" to save your custom fields and close the "Custom Fields" dialog box.
- To display your custom fields in the appropriate views (e.g., Gantt Chart, Task Sheet, Resource Sheet), right-click on a column header and choose "Insert Column" from the context menu. In the "Insert Column" dialog box, scroll down and select your custom field from the list. Click "OK" to add the column to the view.
Here are some great use cases!
- Risk Level: Establish a custom field to assess and track the risk level of individual tasks or entire projects. Assigning a risk level helps you identify and manage high-risk activities, ensuring appropriate mitigation measures are in place.
- Complexity Rating: Use a custom field to evaluate the complexity of tasks or projects. By assigning a complexity rating, you can allocate resources, time, and attention based on the level of complexity, ensuring adequate planning and execution.
- Resource Certification: Implement a custom field to track the certification or skill levels of project resources. This allows you to assign resources with the required qualifications to specific tasks, ensuring the right expertise is utilized.
- Approval Status: Establish a custom field to track the approval status of tasks, deliverables, or project phases. This provides visibility into the approval process, ensuring timely review and sign-off on critical project components.
- RAG status: Create a field that shows a red, amber or green circle depending on the status of a task. You can use whatever metric you like to drive the status. A common use case is cost or progress against baseline.
6. Critical Path Highlighting
Microsoft Project offers a built-in feature called "Critical Path" that helps identify the tasks that directly impact the project's overall duration. However, there is a hidden capability to highlight the critical path directly on the Gantt Chart, making it easier to visualize and analyze.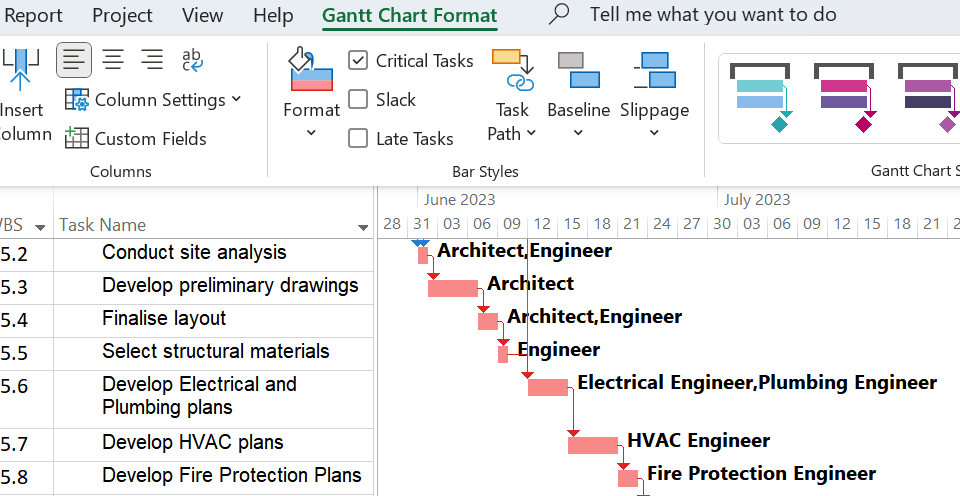
How to view the Critical Path
To enable critical path highlighting, follow these steps:- Open your project in Microsoft Project.
- Go to the "Gantt Chart Format" tab in the ribbon at the top of the window.
- Check the "Critical Path" tick box in the "Bar Styles" group.
7. Network Diagram View
Visualize the relationships between tasks in a flowchart-like format to better understand task dependencies and the critical path.To use the Network Diagram view in Microsoft Project and visualize task dependencies and the flow of activities in your project, follow these steps:
- Open your project in Microsoft Project.
- Go to the "View" tab in the ribbon at the top of the window.
- In the "View" tab, click on the "Network Diagram" button in the "Task Views" group. This will switch your view to the Network Diagram.


To adjust the layout and appearance of the Network Diagram, go to the "Format" tab in the ribbon. Here you can modify the appearance of the boxes, arrows, and text labels, as well as the overall layout and spacing.
To add or remove columns of information in the Network Diagram, right-click on a task box, select "Layout," and choose "Box Styles." In the "Box Styles" dialog box, you can select the desired columns to display or hide.
To filter the tasks shown in the Network Diagram, go to the "View" tab and click on the "Filter" button in the "Data" group. Here you can apply filters to show specific tasks based on criteria such as dates, resource assignments, or task names.
You can also customize the Network Diagram further by using different layout templates, applying different color schemes, or modifying the display options in the "Network Diagram Format" tab.
The Network Diagram view in Microsoft Project provides a visual representation of the task dependencies and critical path in your project. It helps you understand the sequence and flow of activities, identify potential bottlenecks or delays, and optimize the project schedule. By utilizing the features and customization options in the Network Diagram view, you can gain insights into the project's structure and make informed decisions to ensure a successful project execution.
8. Earned Value Analysis
Measure project performance using earned value management (EVM) metrics, which help you track cost and schedule variances, as well as forecast future project performance.
- Set the baseline: Before you can perform earned value analysis, you need to set a baseline for your project. A baseline is a snapshot of the planned schedule, work, and cost at a specific point in time. To set a baseline:
- a. Go to the "Project" tab.
- b. Click on "Set Baseline" in the "Schedule" group.
- c. Choose "Set Baseline" from the dropdown menu.
- d. Select the baseline you want to set (usually Baseline0), then click "OK."
- Update the project progress: To get accurate earned value metrics, you need to update the progress of your project tasks by entering actual start dates, actual finish dates, actual work, and actual cost. You can do this by either:
- a. Double-clicking on a task to open the "Task Information" dialog and entering the actual data.
- b. Adding Actual Start and Actual Finish fields to the task table and updating them.
- c. Using the "Percentage complete" or "Mark on Track" features in the "Task" tab.
- Display earned value columns: To view earned value metrics, you need to add the relevant columns to your task table. Right-click on the column header where you want to insert a new column, then choose "Insert Column" and select the earned value field you want to display. Some common earned value fields include:
- BCWS (Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled): The planned value (PV) of work.
- BCWP (Budgeted Cost of Work Performed): The earned value (EV) of work.
- ACWP (Actual Cost of Work Performed): The actual cost (AC) of work.
- CV (Cost Variance): The difference between EV and AC.
- SV (Schedule Variance): The difference between EV and PV.
- CPI (Cost Performance Index): A ratio of EV to AC, used to measure cost efficiency.
- SPI (Schedule Performance Index): A ratio of EV to PV, used to measure schedule efficiency.
- Analyze the earned value metrics: Once you have the earned value columns displayed, you can analyze the performance of your project. Negative cost or schedule variance indicates that the project is over budget or behind schedule. A CPI of less than 1 means the project is over-budget. SPI value less than 1 indicates that the project is behind schedule (running late).
9. Resource Leveling
Automatically adjust the allocation of resources to tasks to resolve overallocation and optimize the project schedule. To perform resource leveling in Microsoft Project and balance the workload of resources across tasks, follow these steps:- Open your project in Microsoft Project.
- Go to the "Resource" tab in the ribbon at the top of the window.
- In the "Resource" tab, click on the "Leveling Options" button in the "Level" group. This will open the resource leveling options.
- In the "Leveling" dialog box, you have several options to control how the resource leveling is performed. Adjust the settings according to your needs. Here are some key options:
- Leveling calculation: Decide if leveling should be automatic or manual and whether overallocations should be identified on a Minute by Minute, Day by Day, Week by Week basis
- Leveling range: Specify the date range within which you want the leveling to occur.
- Leveling order: Choose the order in which resources should be leveled (e.g., by priority or ID), and select if: leveling should only be within available slack, if it can adjust task assignements, and if it can create splits in remaining work.
- Once you have set the desired leveling options, click "OK" to start the resource leveling process. Microsoft Project will analyze the resource assignments and make adjustments to balance the workload.
Once the resource leveling is complete, Microsoft Project will make adjustments to the task scheduling, such as changing task start or finish dates, assigning additional resources, or splitting tasks if necessary.
Resource leveling will introduce schedule changes, so it's important to review the adjusted schedule and assess any potential impacts on project deadlines or dependencies.
Note: Resource leveling is an iterative process, and you may need to fine-tune the leveling options or make manual adjustments to achieve the desired resource allocation and schedule balance.
10. Auto Filter
Apply filters to specific columns in your project to quickly find and focus on the information you need, such as tasks under a particular phase, tasks of x days and over, or tasks assigned to a particular resource.

