Stakeholders are sometimes divided into primary stakeholders, or those who have a direct stake in the organization and its success, and secondary stakeholders, or those who may be very influential, especially in questions of reputation, but whose stake is more representational than direct. Stakeholder Research Associates Canada Inc. 2005, p. 11 - 13
Common categorisations used for segmenting Stakeholders are:
- Internal vs. External Stakeholders
- Primary vs. Secondary Stakeholders
- Voluntary vs. Involuntary Stakeholders
What is a Primary Stakeholder?
For Clarkson a Primary Stakeholder group is one that the corporation is dependent on for its survival. Five groups of Stakeholders fall into the Primary Stakeholder category:- investors and shareholders,
- employees, customers,
- suppliers, and
- a Public group of governments and communities who control infrastructure, markets and who require laws to be followed and taxes to be paid.
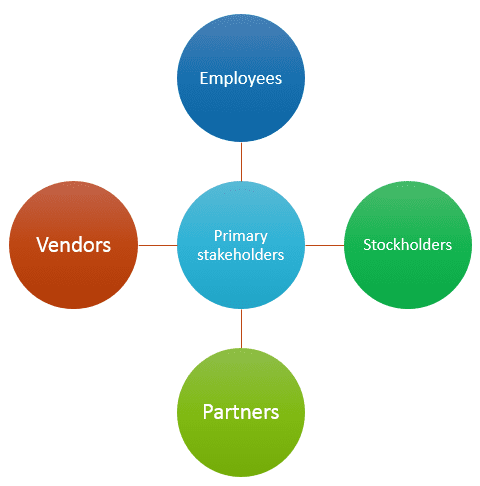
Primary Stakeholders as:who have a stake in the organization's success.
- employees,
- stockholders,
- vendors and
- partners
Example Primary Stakeholders
Primary Social and Non-social Stakeholders
Wheeler and Sillanpaa take their categorization a step further splitting Primary Stakeholders into social and non-social. Primary Social Stakeholders are:- Shareholders and investors
- Employees and managers
- Customers
- Local communities
- Suppliers and other business partners
- Natural environment
- Future generations
- Nonhuman species
For me Stakeholder Research Associates Canada Inc. provide the clearest definition of primary and secondary stakeholders
Stakeholders are sometimes divided into primary stakeholders, or those who have a direct stake in the organization and its success, and secondary stakeholders, or those who may be very influential, especially in questions of reputation, but whose stake is more representational than direct.Read more on other stakeholder categories:
Secondary stakeholders can also be surrogate representatives for interests that cannot represent themselves, i.e., the natural environment or future generations. Stakeholder Research Associates Canada Inc. 2005, p. 11 - 13
Primary Stakeholders - references
Bucholtz, A. K. and Carroll, A. B. 2012. Business and Society , Ethics and Stakeholder Management. 8th edition. South-Western. Cengage Learning. Latest editionDavid Wheeler and Maria Sillenpaa. 1997. The Stakeholder Corporation: A Blueprint for Maximizing Stakeholder Value London: Pitman Publishing.
Max B. E. Clarkson. 1995. A Stakeholder Framework for Analyzing and Evaluating Corporate Social Performance. The Academy of Management Review, Vol. 20, No. 1 (Jan., 1995), pp. 92-117. [online] https://www.jstor.org/stable/258888 [Accessed 22 July 2016].
Stakeholder Research Associates Canada Inc. 2005. The Stakeholder Engagement Manual. VOLUME 1: THE GUIDE TO PRACTITIONERS' PERSPECTIVES ON STAKEHOLDER ENGAGEMENT. [pdf] Canada: Stakeholder Research Associates Canada Inc. Available at: https://www.accountability.org/images/content/2/0/207.pdf
Chiu, P. 2009. Looking Beyond Profit: Small Shareholders and the Values Imperative. Abingdon: Routledge. p. 33.
Read more on Stakeholder Management
Stakeholder analysis templates in Word, Visio and Excel.Stakeholder Management ebook
Happy Stakeholders - Pleasure and Displeasure List
Stakeholders - who are the Key Players? - Some Stakeholders are really important. How do you find them and get them on your side before they can do any damage?
Stakeholder mindmap - a mindmap showing Stakeholders for an IT project.
Stakeholder Salience - an overview of the stakeholder salience model.


