Table of Contents:
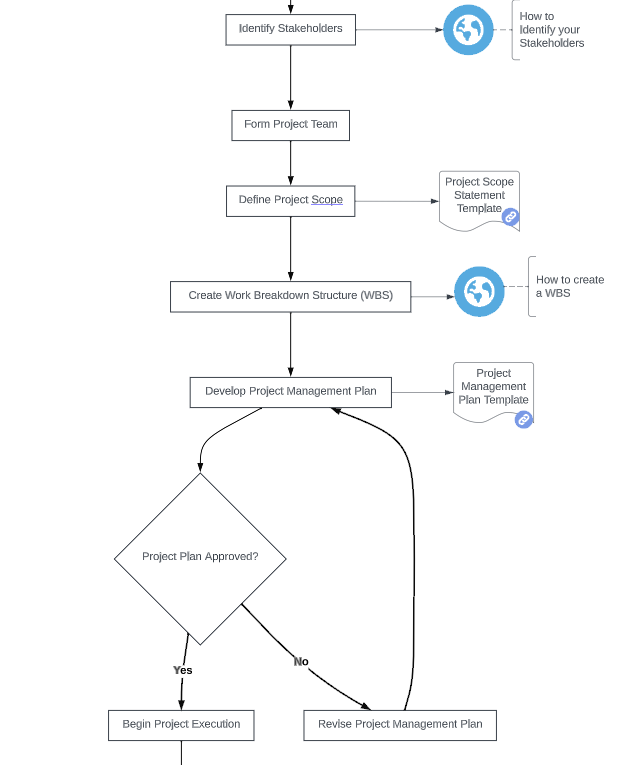
What does the flow chart show?
It begins with the creation of a Statement of Work, a crucial document that defines the project's objectives and scope. Following this, the process involves developing a Project Charter and identifying stakeholders, ensuring that all key parties are recognized and their interests are considered from the outset.The chart then guides the user through forming the project team, defining the project scope with a clear statement, and creating a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to organize and define the total scope of the project. The subsequent step involves developing a detailed Project Management Plan, essential for guiding the project's execution and monitoring.
A critical decision point in the flowchart is the approval of the Project Plan. If approved, the project moves into the execution phase. If not, the plan is revised. This iterative approach ensures that the project plan is robust and comprehensive.
The flowchart also includes steps for setting up the project infrastructure, developing a project schedule, allocating resources, planning for risk management, establishing project controls, and conducting a kick-off meeting. These elements are fundamental in ensuring that the project is well-planned, resources are efficiently utilized, and risks are effectively managed.
The flowchart concludes with the completion of the Project Start-up Phase, marking the transition to the next phase of the project lifecycle. This phase is critical for laying a solid foundation for the project, ensuring that it is well-planned, organized, and prepared for successful execution. The flowchart serves as a valuable tool for project managers, providing a clear and structured pathway for initiating projects effectively
Breakdown of the symbols in the flow chart
| Text | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Statement of Work | Document |
| Develop Project Charter | Activity |
| Identify Stakeholders | Activity |
| Project Charter Template | Resource/Template |
| How to Identify your Stakeholders | Guide/Instructions |
| Form Project Team | Activity |
| Define Project Scope | Activity |
| Project Scope Statement Template | Resource/Template |
| Create Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) | Activity |
| How to create a WBS | Guide/Instructions |
| Develop Project Management Plan | Activity |
| Project Management Plan Template | Resource/Template |
| Project Plan Approved? | Decision Point |
| Begin Project Execution | Activity (Conditional) |
| Revise Project Management Plan | Activity (Conditional) |
| Set up Project Infrastructure | Activity |
| Develop Project Schedule | Activity |
| Allocate Resources | Activity |
| Risk Management Planning | Activity |
| Establish Project Controls | Activity |
| Conduct Kick-off Meeting | Activity |
| Project Start-up Phase Complete | Milestone |
Description of each step in the process
The "Project Start-Up Phase" flowchart details a series of steps essential for initiating a project effectively. Here is a description and explanation of each step:- Statement of Work: This is a document that clearly defines the project's objectives, scope, and deliverables. It sets the groundwork for what the project aims to achieve.
- Develop Project Charter: An activity where the project charter is created. The charter formally authorizes the project and provides a high-level overview, including the project's purpose, objectives, and stakeholders.
- Identify Stakeholders: This step involves identifying all individuals, groups, or organizations that could affect or be affected by the project. It's crucial for ensuring all potential impacts and interests are considered. Learn more about how to Identify Stakeholders.
- Form Project Team: This activity involves assembling the team that will work on the project, ensuring that it has the right mix of skills and expertise.
- Define Project Scope: In this step, the scope of the project is defined and documented. A clear project scope statement is crucial for setting boundaries and expectations.
- Create Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): This involves breaking down the project into smaller, more manageable components. A WBS helps in organizing and defining the total scope of the project. Free to download - example Work Breakdown Structures. Get a WBS template in Excel.
- Develop Project Management Plan: An activity where the comprehensive plan for managing the project is developed. This plan covers aspects like scope, schedule, cost, quality, resources, and risk management. Get a Project Management Plan template.
- Project Plan Approved?: A decision point where it's determined whether the project plan is approved to proceed. If yes, the project moves to the execution phase; if no, the plan needs revision.
- Begin Project Execution (Conditional): This step is taken if the project plan is approved, marking the start of the project's execution phase.
- Revise Project Management Plan (Conditional): If the project plan is not approved, it is revised in this step. This ensures that the plan meets all necessary requirements and standards. Get a Risk Management Plan template.
- Set up Project Infrastructure: This involves establishing the necessary infrastructure for the project, including physical and IT resources.
- Develop Project Schedule: The creation of a detailed schedule outlining when and how the project's tasks will be performed.
- Allocate Resources: This step involves distributing the necessary resources (human, financial, material) effectively across the project.
- Risk Management Planning: An activity where strategies to identify, analyze, and manage project risks are developed.
- Establish Project Controls: Setting up mechanisms to monitor and control the project, ensuring it stays on track with its objectives.
- Conduct Kick-off Meeting: A meeting to officially start the project, bringing together the project team and stakeholders to align on objectives, expectations, and roles.
- Project Start-up Phase Complete: This marks the completion of the start-up phase and the transition to subsequent phases of the project lifecycle.

